Table of Contents
How to Integrate AI Chatbots for Patient Support
Clinics can integrate AI chatbots by selecting a HIPAA-compliant platform and connecting it to their website or patient portal. This patient support automation tool handles tasks like appointment scheduling, answering billing FAQs, and sending reminders, freeing up staff while ensuring data privacy through a Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
What Is an AI Chatbot in Healthcare?
An AI chatbot in healthcare, also known as a clinic virtual assistant or medical AI assistant, is a software program designed to simulate human conversation with patients. It uses advanced technologies like Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) to understand and respond to patient queries via text or voice, augmenting human care by providing instant responses and triaging patients.
Unlike simple, scripted bots, modern AI chatbots can interpret complex questions, learn from interactions, and provide context-aware answers. They act as a digital front door to your clinic, available 24/7 to assist with administrative and informational needs.
Real-World Examples in a Clinic Setting:
- Appointment Management: A patient can ask, “Are there any openings with Dr. Smith next Tuesday afternoon?” The chatbot checks the schedule and offers available slots.
- Answering FAQs: Instead of calling, a patient types, “What are your clinic’s hours?” or “Do you accept my insurance?” and receives an instant, accurate response.
- Post-Visit Follow-ups: A chatbot can send a message a few days after a visit: “Hi [Patient Name], this is a reminder to take your prescribed medication. Do you have any questions about your follow-up instructions?”
These tools are not designed to replace healthcare professionals but to augment their capabilities by automating repetitive tasks, thereby improving efficiency and patient access to information.

Why Your Clinic Needs an AI Chatbot in 2026
The healthcare landscape in 2026 is defined by rising patient expectations, significant administrative burdens, and persistent staff shortages. AI chatbots directly address these challenges, moving from a “nice-to-have” technology to an essential component of modern clinic operations.
Tackling Staff Burnout and Patient Load
Healthcare providers are overburdened. Studies show physicians can spend hours each day on administrative work, including documentation and answering patient queries. This contributes to burnout and reduces time for direct patient care. According to the American Medical Association, two-thirds of physicians reported using AI in 2024 to improve work efficiency.
An AI healthcare chatbot automates these high-volume, low-complexity tasks. Research shows that AI chatbots can handle up to 80% of routine healthcare questions, freeing up front-desk staff and nurses to focus on more complex patient needs and clinical duties.
Providing 24/7 Patient Support
A patient’s health questions don’t stop when your clinic closes. An OpenAI analysis found that most health-related conversations on its platform happen outside typical 8 AM to 5 PM clinic hours, underscoring a significant gap in patient support.
A clinic virtual assistant provides round-the-clock availability, allowing patients to book appointments, get answers to billing questions, or receive pre-visit instructions at their convenience. This improves patient satisfaction and ensures continuous engagement.
Driving Significant Cost Reduction
The financial benefits of patient support automation are substantial. By deflecting routine calls from front-desk staff, clinics can optimize resource allocation. One healthcare organization reported saving $2.40 million in its first year through new patient revenue and reduced contact center calls.
Furthermore, automated appointment reminders have been shown to slash no-show rates from as high as 35% down to 6%. Filling these empty slots directly translates to recovered revenue and a more efficient schedule.
Improving Patient Satisfaction and Engagement
In today’s digital world, patients expect immediate, accessible service. Long phone hold times and delayed email responses lead to frustration. AI chatbots offer instant answers and self-service options, which directly correlates with a better patient experience.
By providing tools for remote engagement, such as symptom tracking or follow-up questionnaires, clinics can keep patients connected to their care plans between visits, improving outcomes, especially in chronic disease management.
Key Patient Support Use-Cases for AI Chatbots
A well-implemented medical AI assistant can handle a wide range of non-clinical tasks. Here are the most impactful use-cases for a modern clinic:

- Appointment Booking & Reminders: Allows patients to schedule, reschedule, or cancel appointments 24/7. Automated reminders via SMS or WhatsApp have been proven to reduce no-show rates by over 50%.
- Pre-Visit Instructions & Digital Check-In: Delivers customized instructions before an appointment (e.g., “Please remember to fast for 8 hours before your blood test”). It can also facilitate digital check-in, reducing wait times by up to 40% by handling paperwork in advance.
- Post-Treatment Follow-ups: Automates follow-up messages to check on a patient’s recovery, gather feedback, and ensure they understand their care plan. This is crucial for post-discharge care and chronic condition management.
- Medication Reminders & Adherence: Sends timely reminders for patients to take their medications, improving adherence, which is a major factor in treatment success. This is particularly valuable for patients with complex medication schedules.
- Insurance & Billing FAQs: Answers common, repetitive questions about insurance coverage, billing codes, and payment options. OpenAI data shows users send nearly 2 million messages a week about health insurance, indicating a high demand for this information.
- Non-Emergency Triage & Guidance: Guides patients by asking a series of questions about their symptoms to recommend the appropriate level of care (e.g., “This sounds like something you should discuss with your GP,” or “These symptoms may require urgent attention. Please visit the nearest emergency room.”). A clinical study found one leading AI’s triage advice was safe 97% of the time, slightly higher than human doctors (93.1%).
Tools Used for Healthcare Chatbots: ChatGPT vs. Med-PaLM
Choosing the right AI engine is fundamental to your chatbot’;s success. While many platforms exist, the conversation is often dominated by two powerhouses: OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Med-PaLM. It’s crucial to understand their distinct strengths and intended use cases, especially their enterprise-grade, HIPAA-compliant versions.
ChatGPT (via OpenAI for Healthcare)
Best For: Administrative automation, patient communication, and workflow efficiency.
- HIPAA Compliance: OpenAI offers an enterprise-level platform, “OpenAI for Healthcare,” which is HIPAA-compliant and includes a Business Associate Agreement (BAA). Standard consumer ChatGPT is not HIPAA-compliant.
- Strengths: Excels at natural, empathetic conversation. A 2025 systematic review found that ChatGPT was often perceived as more empathic than human practitioners in text-based interactions. It’s ideal for drafting patient education materials, summarizing notes, and handling administrative queries.
- Use Case: Powering a website chatbot to answer billing questions, generate discharge summaries from clinician notes, or create multilingual patient instructions.
Med-PaLM 2 (Google)
Best For: Clinical question answering, diagnostic support (for clinicians), and evidence-based reasoning.
- HIPAA Compliance: Deployed through Google Cloud AI Healthcare, which supports HIPAA compliance with a BAA.
- Strengths: Specifically fine-tuned on a massive corpus of medical data. It achieved an 86.5% accuracy score on the MedQA (USMLE-style) benchmark, demonstrating expert-level medical knowledge. It is designed for high-stakes clinical reasoning.
- Use Case: A clinician-facing tool to find differential diagnoses, summarize the latest research on a rare condition, or answer complex clinical questions with citations. While it can power patient-facing bots, its core strength is deep medical accuracy.
For clinical AI chatbot innovations beyond patient support tasks, see our article on how AI voice biomarkers and chatbot technologies are being used to detect early disease signs for conditions like Parkinson’s and depression.
When to Use ChatGPT vs. Med-PaLM
Think of it as a Generalist vs. a Specialist.
Use an enterprise solution powered by ChatGPT (GPT-4 and newer models) for patient-facing administrative tasks. Its conversational ability and proven performance in generating empathetic, easy-to-understand text make it perfect for scheduling, FAQs, and patient education.
Use Med-PaLM 2 when the primary need is deep, validated medical knowledge. While a patient-facing bot could use it to answer health questions (with extreme caution and disclaimers), its true value is as a “doctor’s assistant,” helping clinicians with complex reasoning. A 2025 study comparing models found Med-PaLM 2 was judged significantly safer than general-purpose LLMs for medical use cases.
Other Platforms to Consider:
- WhatsApp Chatbots: Leverage the world’s most popular messaging app for reminders and simple interactions.
- Website Chat Widgets: The most common integration, providing an immediate point of contact on your clinic’s site.
- EMR-Integrated Bots: Platforms that connect directly to your Electronic Medical Record (EMR) system for personalized interactions, like pulling up appointment history or lab results (requires robust security).
Step-by-Step: How to Integrate an AI Chatbot in Your Clinic
Implementing a clinic virtual assistant doesn’t have to be a complex coding project. Many modern platforms offer no-code solutions. Here is a beginner-friendly, seven-step process to get started.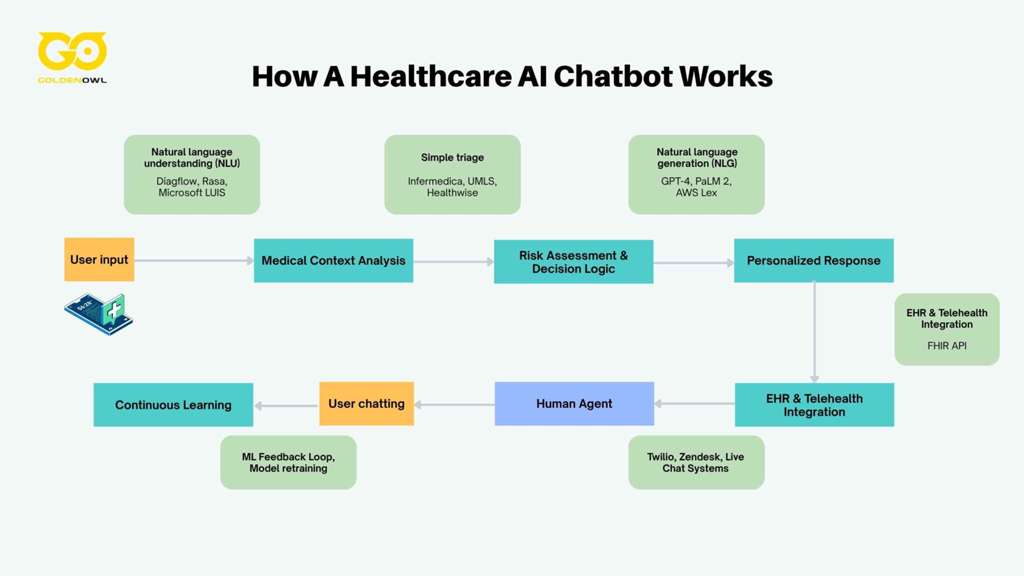
Step 1: Identify Key Patient Interaction Points
Start by analyzing where your staff spends the most time on repetitive tasks. Is it answering phone calls for appointments? Responding to emails about insurance? These are your highest-impact areas for automation.
Step 2: Choose Your Platform (Website, WhatsApp, etc.)
Decide where your patients will interact with the bot. A website widget is a great starting point. If your patients are active on WhatsApp, a chatbot on that platform can be highly effective for reminders and quick questions.
Step 3: Select an AI Engine or Pre-Built Solution
You can choose a HIPAA-compliant chatbot provider that has already integrated a powerful AI engine (like GPT-4). This is the easiest route. Alternatively, your IT team could use the OpenAI API for Healthcare to build a custom solution.
Step 4: Design Safe Prompts and Guardrails (Crucial for Safety)
This is the most important step. You must define what your chatbot can and cannot do. Program it with clear “guardrails.” For example, if a user types symptoms of a heart attack, the bot’s only response should be to direct them to emergency services immediately. It should never attempt a diagnosis.
Step 5: Connect to Your Appointment System
For scheduling, the chatbot needs to connect to your clinic’s calendar or EMR scheduling module. Most modern chatbot platforms offer pre-built integrations or use APIs to make this connection securely.
Step 6: Test Rigorously with Real Patient Scenarios
Before going live, test the chatbot with a wide range of real (but anonymized) patient questions. Try to “break” it. Ask it questions outside its scope. This helps you refine its responses and strengthen its guardrails.
Step 7: Go Live, Monitor Performance, and Gather Feedback
Start with a phased rollout, perhaps only activating the chatbot for a few hours a day. Monitor key metrics: How many queries does it resolve? How often does it escalate to a human? What are patients saying about it? Use this feedback to continuously improve its performance.
Data Privacy, Ethics & Compliance: The Non-Negotiable Foundation
When integrating any AI tool in healthcare, compliance is not an afterthought—it is the starting point. Mishandling Protected Health Information (PHI) can lead to severe penalties, loss of patient trust, and significant legal risk.
HIPAA Compliance is Mandatory
Any AI tool that interacts with PHI falls under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). To be compliant, your AI solution MUST include:
- Business Associate Agreement (BAA): A signed BAA is a legal contract that requires your AI vendor (the “business associate”) to protect PHI according to HIPAA rules. Using a vendor without a BAA is a direct violation. Consumer tools like the free version of ChatGPT will not provide a BAA.
- End-to-End Encryption: All data must be encrypted both “in transit” (as it moves over the internet) and “at rest” (when stored on servers).
- Access Controls: Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to ensure only authorized personnel can view sensitive data.
- Audit Trails: The system must log all access and actions performed on PHI for monitoring and investigation purposes.
What a Healthcare Chatbot Should NEVER Do
A patient-facing chatbot’;s scope must be strictly limited to avoid practicing medicine. It should be programmed to refuse and escalate if asked to:
- Provide a diagnosis.
- Recommend a specific treatment or medication.
- Interpret lab results or medical images.
- Offer any form of medical advice that requires clinical judgment.
The Importance of Human Escalation and Consent
A chatbot is not an island. There must be a clear, seamless pathway for a patient to connect with a human at any time. This “human-in-the-loop” model is essential for safety and user satisfaction.
Finally, transparency is key. Always inform patients that they are interacting with an AI assistant. A simple disclaimer like, “You are speaking with our automated assistant. I can help with scheduling and FAQs but cannot provide medical advice,” builds trust and manages expectations.
4 Common Mistakes Clinics Make When Adopting AI Chatbots
Avoiding common pitfalls can be the difference between a successful AI integration and a frustrating failure. Here are four key mistakes to watch out for.
1. Using the Chatbot as a Doctor
The biggest mistake is programming the bot to answer questions beyond its scope. A medical AI assistant should be a scheduler and an information clerk, not a diagnostician. Its primary role is to navigate patients to the right human expert efficiently.
2. Having No Fallback to Human Staff
An AI that hits a dead end with no option to “talk to a person” creates a terrible patient experience. A seamless escalation path to your front-desk staff via live chat, a callback request, or a phone number is non-negotiable.
3. Poor Prompt and Guardrail Design
Vague instructions or weak safety guardrails can lead to the chatbot providing incorrect, irrelevant, or even dangerous information. Invest time in meticulously defining the bot’s purpose, personality, and limitations.
4. Attempting to Over-Automate Empathetic Conversations
While models like GPT-4 can generate empathetic-sounding text, they cannot replicate genuine human connection. Do not try to automate complex, sensitive conversations, such as discussing a difficult diagnosis or handling a patient complaint. These moments require a human touch.
Cost vs. ROI: The Financial Case for Patient Support Automation
Investing in AI technology requires a clear understanding of both the costs and the expected returns. The ROI of a clinic virtual assistant extends far beyond direct financial savings.
Understanding the Costs
The cost of implementing an AI chatbot can vary widely based on your approach:
- Subscription (SaaS) Models: Many vendors offer pre-built, HIPAA-compliant chatbots for a monthly fee, often ranging from $15 to $400+ per month per user/agent. Some charge per resolution (e.g., $0.69 per resolved query). This is the most accessible option for small to medium clinics.
- Custom Development: Building a bespoke chatbot from scratch can cost anywhere from $15,000 to over $100,000, depending on complexity and integrations.
- Hidden Costs: Don’t forget to budget for data preparation, integration with your EMR (which can cost $25,000+ for analysis alone on legacy systems), staff training, and ongoing maintenance.
Measuring the Return on Investment (ROI)
A holistic ROI model for healthcare AI includes four key dimensions:
- Operational Efficiency: This is the most immediate return. It includes time saved by staff on administrative tasks, reduced documentation burden, and optimized schedules. AI scribes, for example, have been shown to reduce physician documentation time by up to 60%.
- Financial Return: This includes direct cost savings from automating tasks and increased revenue from reducing patient no-shows. Filling 75-85% of canceled slots can have a major impact on your bottom line.
- Patient Experience & Satisfaction: While harder to quantify, improved patient satisfaction from 24/7 access and instant responses leads to better retention and positive reviews, which are valuable assets for any clinic.
- Clinical Outcomes & Safety: For administrative chatbots, this is an indirect benefit. By improving medication adherence through reminders and ensuring patients receive clear follow-up instructions, chatbots contribute to better health outcomes and patient safety.
When viewed through this comprehensive lens, the investment in patient support automation provides clear, multi-faceted value that strengthens a clinic’s clinical and financial health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is an AI chatbot safe for patients?
Yes, when implemented correctly. A safe AI chatbot is one used for non-clinical tasks like scheduling and FAQs. It must be HIPAA-compliant, have strong safety guardrails to prevent it from giving medical advice, and always provide an easy way to escalate to a human.
Can AI replace my front desk staff?
No. The goal of a medical AI assistant is to augment, not replace, your staff. It handles the repetitive, high-volume queries, which frees your skilled human staff to focus on complex patient issues, provide in-person assistance, and manage tasks that require empathy and critical thinking.
Is Med-PaLM better than ChatGPT for healthcare?
They are better at different things. Med-PaLM 2 is a specialist, superior for tasks requiring deep clinical knowledge and accuracy, making it ideal for clinician support. Enterprise versions of ChatGPT (GPT-4 and above) are generalist powerhouses, excelling at natural conversation, administrative automation, and patient communication, making them better suited for patient-facing support roles.
Can small clinics afford AI chatbots?
Absolutely. The rise of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models means small clinics can access powerful, HIPAA-compliant chatbots for a predictable monthly subscription fee (some starting as low as $15/agent/month) without a large upfront investment in custom development. This makes the technology highly accessible.
Do chatbots give medical advice?
No, and they never should. A responsibly designed healthcare chatbot is explicitly programmed to avoid giving medical advice, diagnoses, or treatment recommendations. Its role is to provide information and navigation, guiding patients to the appropriate human healthcare professional for all clinical matters.
4 Common Mistakes Clinics Make When Adopting AI Chatbots
Avoiding common pitfalls can be the difference between a successful AI integration and a frustrating failure. Here are four key mistakes to watch out for.
1. Using the Chatbot as a Doctor
The biggest mistake is programming the bot to answer questions beyond its scope. A medical AI assistant should be a scheduler and an information clerk, not a diagnostician. Its primary role is to navigate patients to the right human expert efficiently.
2. Having No Fallback to Human Staff
An AI that hits a dead end with no option to “talk to a person” creates a terrible patient experience. A seamless escalation path to your front-desk staff via live chat, a callback request, or a phone number is non-negotiable.
3. Poor Prompt and Guardrail Design
Vague instructions or weak safety guardrails can lead to the chatbot providing incorrect, irrelevant, or even dangerous information. Invest time in meticulously defining the bot’s purpose, personality, and limitations.
4. Attempting to Over-Automate Empathetic Conversations
While models like GPT-4 can generate empathetic-sounding text, they cannot replicate genuine human connection. Do not try to automate complex, sensitive conversations, such as discussing a difficult diagnosis or handling a patient complaint. These moments require a human touch.
Final Takeaway: Your Partner in Patient Support, Not a Replacement
Integrating an AI chatbot into your clinic in 2026 is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a practical strategy for enhancing efficiency, managing costs, and meeting modern patient expectations. These tools are powerful allies, designed to serve as a support system for your dedicated staff, not as a replacement for them.
By automating the routine, you empower your team to focus on the essential: providing compassionate, high-quality human care. The key to success lies in a responsible, phased adoption—starting with low-risk administrative tasks and prioritizing patient safety and data privacy above all else.
As a healthcare technology professional, I work with clinics and medical teams to implement AI chatbots on WordPress websites that support patients responsibly—covering chatbot design, WordPress websites development, integration, and long-term optimization. If you need to connect with me please comment or contact me.
