Introduction: From Healthcare Excellence to a Digital Health Revolution
For decades, Singapore has stood as a global benchmark for healthcare excellence, with world-class hospitals and one of the longest life expectancies worldwide. Yet the nation isn’t content to rest on past achievements. Confronting an aging population and rising healthcare costs, Singapore is leading a digital revolution centered on Smart Hospitals in Singapore — high-tech, human-centric facilities that blend AI, robotics, and data to make care more predictive, personalized, and efficient.
This article explores how Singapore’s smart hospital model is transforming healthcare. We’ll break down its core philosophies, real-world innovations, and the lessons global healthcare leaders can learn from the Lion City’s leap into the future.

Table of Contents
The Singaporean Blueprint: More Than Just Technology
What truly defines a Smart Hospital in Singapore goes beyond advanced gadgets or automation—it’s a patient-first philosophy. These hospitals use data, AI, and digital systems to redesign care models that revolve around individual needs. At the forefront, Singapore General Hospital (SGH) has built its vision on three powerful pillars—Smart Treatment, Smart Services, and Smart Management—creating a blueprint that’s reshaping healthcare for the future.
Smart Treatment: Engineering Excellent Patient Outcomes
This pillar is dedicated to deploying smart solutions to achieve superior clinical results. It involves looking across all major service lines—outpatient, inpatient, emergency, and surgical—to identify areas where technology can fundamentally transform care delivery. The focus is on precision, safety, and efficacy.
- Surgical Planning and Rehearsal: Surgeons at SGH utilize 3D-printed, patient-specific anatomical models to plan and rehearse complex surgeries, enhancing precision and reducing risks.
- Holomedicine and Extended Reality (XR): The hospital has ventured into the realm of holomedicine, using XR technologies not only for surgical planning but also for immersive patient education, helping individuals better understand their conditions and treatment plans.
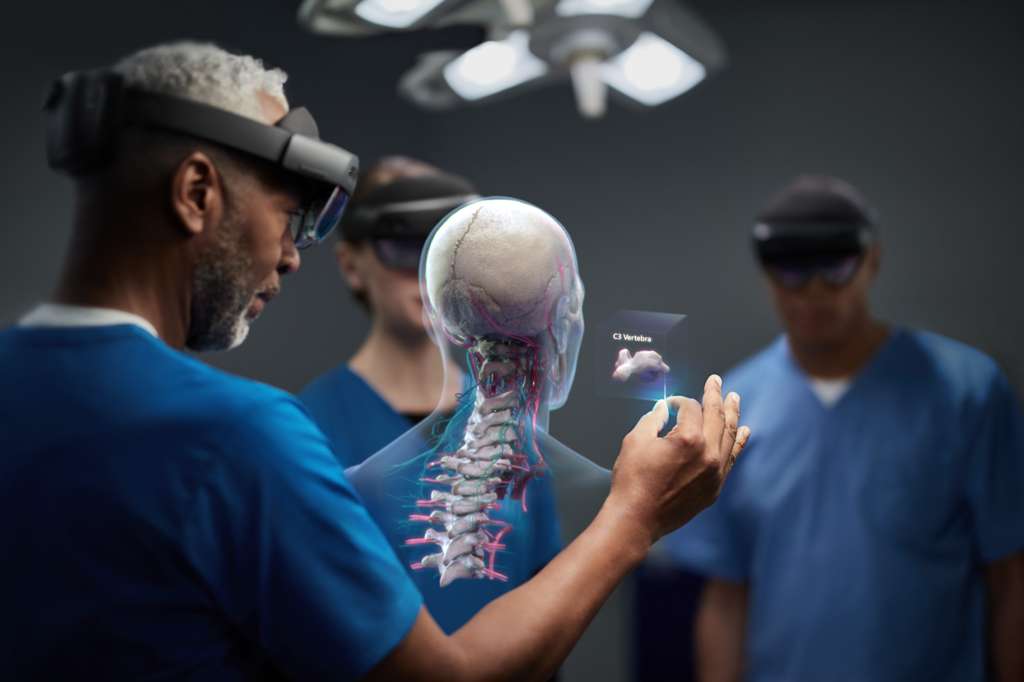

Smart Services: Enhancing the Human Experience
The second pillar of Smart Hospitals in Singapore focuses on enhancing the experience of both patients and healthcare staff through intelligent, human-centered technology. Efficiency here never replaces empathy—it amplifies it. A standout example is the MyCare app, integrated into bedside tablets across the SingHealth network. This app empowers patients with instant access to their health data, test results, and daily care schedules while allowing them to send simple service requests—like calling for assistance or ordering beverages—directly to nurses’ mobile devices. The result is faster response times, smoother workflows, and a more personalized hospital experience for every patient.
Smart Management: Creating Integrated and Efficient Operations
The final pillar leverages technology to build integrated, seamless, and highly efficient hospital operations. This is about creating a “digital nervous system” for the hospital. A key initiative under this pillar is the development of a “digital twin” of the hospital. According to Geoffrey Gui, Director of SGH’s Future Health Systems department, this aims to create a virtual mirror and a “digital record of what’s happening in the hospital.”
This virtual replica can be used for real-time operational oversight, optimizing resource allocation (like beds and operating theaters), streamlining supply chains, and enabling smarter facility management. It represents a shift from reactive problem-solving to proactive, data-driven operational control .
The Engine Room: A Deep Dive into the Technologies Powering Singapore’s Smart Hospitals
The Singaporean smart hospital vision is powered by a sophisticated ecosystem of interconnected technologies. This section delves into the specific applications of Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and the underlying digital infrastructure that form the engine of this transformation.
As Smart Hospitals in Singapore adopt AI, robotics, and IoT at scale, the demand for skilled healthcare professionals who can integrate and manage these technologies is rapidly rising. Building future-ready teams is as crucial as building smart infrastructure. To understand which capabilities will define healthcare success in the coming years, explore our detailed guide — Top Healthcare Tech Skills to Learn in 2025.
Artificial Intelligence: The Brain of the Operation
AI is arguably the most critical enabler, acting as the intelligent core that processes vast amounts of data to drive prediction, automation, and diagnosis.
Predictive Analytics & Early Diagnosis
Singapore is moving decisively from reactive to predictive care, using AI to identify health risks before they become critical. A landmark example is the pilot program for managing Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD).
Case Study: Digital Twins for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
In early 2025, SGH and Tan Tock Seng Hospital (TTSH) were to trial a digital twin technology developed by health tech start-up Mesh Bio. Singapore has the third-highest incidence of treated end-stage CKD due to diabetes globally . The AI-powered software, HealthVector Diabetes, creates a virtual replica of a patient based on their biological data (blood sugar, cholesterol, BMI, etc.). This “digital twin” can simulate the progression of the disease over three years, allowing doctors to predict the risk of CKD onset. This enables personalized, intensified treatments to delay kidney failure, potentially giving patients an additional 15 years of quality life free from dialysis.
This predictive capability extends to national screening programs. The Singapore Eye Lesion Analyser (SELENA+) is a deep learning AI system used in the national diabetic retinopathy screening program to analyze eye images and detect disease early, addressing a major complication of diabetes which is projected to affect one million Singaporeans by 2050 . Another AI system screens hospital inpatients to identify those at high risk of readmission, allowing for targeted interventions.
Workflow & Documentation Automation
Clinician burnout from endless paperwork is a global challenge, and Smart Hospitals in Singapore are addressing it with cutting-edge Generative AI. The Ministry of Health (MOH) is expanding AI-powered documentation tools across public hospitals to automate record summarization and routine data entry by 2025. At the National University Health System (NUHS), innovations like MediVoice and Scribe already transcribe speech into medical notes in real time—saving hours of administrative work. Beyond efficiency, this technology allows nurses and doctors to focus on what truly matters: meaningful eye contact, patient interaction, and quality care.

Diagnostic Imaging
In Smart Hospitals in Singapore, AI now assists radiologists by analyzing vast medical images faster and more accurately than ever. The Ministry of Health (MOH) is using platforms like AimSG to streamline breast cancer screening and deploy trusted imaging AI models across hospitals—boosting diagnostic speed, precision, and patient safety.
Robotics and Automation: The Hands and Feet of Modern Care
Robots are no longer science fiction in Singapore’s hospitals. They are a reliable workforce handling routine but essential tasks, allowing their human colleagues to focus on higher-value patient care.
Logistical Automation
In Smart Hospitals in Singapore, automation is redefining hospital logistics. At Singapore General Hospital (SGH), a fleet of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) runs 24/7, delivering medical supplies, lab samples, and surgical instruments across buildings. This innovation reduces manual labor, improves efficiency, and frees healthcare staff for patient-focused tasks. Changi General Hospital (CGH) also uses robots for cleaning and meal delivery, showcasing Singapore’s leadership in smart hospital operations.
Clinical and Surgical Precision
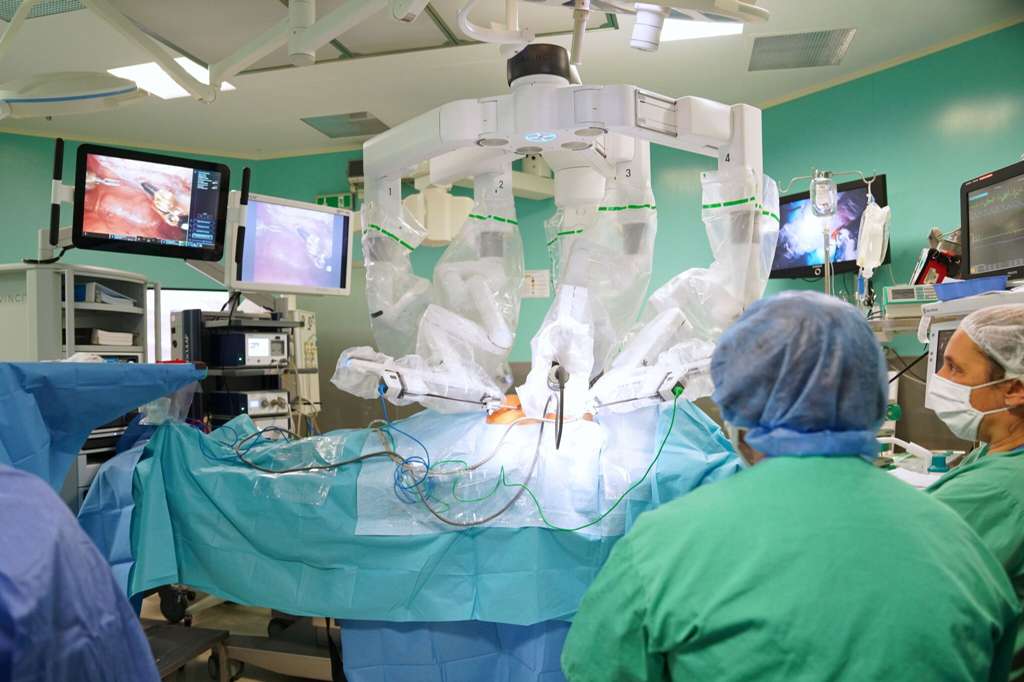
In the operating theater, robotics enhances surgical precision and enables minimally invasive procedures for complex cases.
Case Study: Robotic Surgery for Complex Cancers
Surgical management of endometrial cancer in morbidly obese women is technically challenging. A retrospective analysis at SGH from 2016 to 2023 on 33 patients with a BMI > 40 kg/m² demonstrated that robotic surgery is a safe and effective alternative. The procedure, performed with the da Vinci Surgical System, circumvents the shortfalls of traditional minimally invasive surgery, such as poor visualization and difficult instrument angulation. The study reported an average operative time of 232 minutes, no conversions to open surgery (laparotomy), and a 0% 1-year mortality rate, affirming its reliability for this high-risk patient group .
Beyond cancer, AI-powered algorithms are also being used to enhance procedures like knee replacement surgery, promising faster and more effective outcomes for patients .
IoT and Telehealth: Extending Care Beyond Hospital Walls
The smart hospitals in Singapore is not confined to its physical buildings. Through IoT and telehealth, it extends its reach into the community and patients’ homes, creating a continuum of care.
Remote Patient Monitoring
In Smart Hospitals in Singapore, the Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming patient monitoring. At Ng Teng Fong General Hospital (NTFGH), the VitalScout project uses wearable devices to track patients’ vital signs in real time. Nurses can view this data instantly on mobile devices, enabling quicker interventions, reducing manual checks, and freeing more time for meaningful patient care.
The ‘Phygital’ Hospital and Home-Based Care
In Smart Hospitals in Singapore, the concept of the “phygital” hospital blends physical and digital care. Through the SGH@Home initiative, patients receive hospital-level treatment at home using remote monitoring and telehealth tools. Accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, this shift—supported by government policies and subsidies—has expanded telemedicine for chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension, easing hospital loads and extending care into the community.
Digital Infrastructure: The Central Nervous System
None of these innovations would be possible without a robust, secure, and integrated digital backbone. Singapore has invested heavily in creating a national-level data infrastructure.
- Integrated Electronic Medical Records (EMR): A key strategic goal is the consolidation of EMR systems into a common platform, the Next Generation Electronic Medical Record (NGEMR). This allows for seamless data sharing as a patient moves between different care settings, from a local polyclinic to a specialist hospital, ensuring that clinicians have a complete and up-to-date view of the patient’s history .
- National Data Platforms: The government, in collaboration with the national healthtech agency Synapxe, has established powerful cloud-based platforms. HEALIX (Health Empowerment through Advanced Learning and Intelligent eXchange) serves as an “AI technology factory,” providing secure access to anonymized clinical, genomic, and lifestyle data for training and deploying AI models. Concurrently, TRUST (Trusted Research and Real-World Data Utilisation and Sharing Tech) is a secure platform where researchers can analyze sensitive health data without being able to download it, ensuring patient privacy .
The Human Element: Empowering Clinicians and Engaging Patients
A purely technological focus misses the most crucial element of healthcare transformation: its impact on people. The success of smart hospitals in Singapore is measured not just by efficiency metrics, but by how technology empowers clinicians and engages patients.
Redefining the Role of Nurses and Doctors
A common misconception is that AI and robots will replace healthcare staff—but Smart Hospitals in Singapore prove the opposite. Technology here enhances human capability by automating repetitive tasks, allowing clinicians to focus on decision-making, empathy, and patient care. At NUHS, an AI-driven fall risk assessment tool predicts patients’ risk in real time, helping nurses act faster while reducing paperwork. As Dr. Catherine Koh notes, these tools empower nurses to focus on what matters most—delivering quality care.
Placing the Patient at the Center of Their Care Journey
Digital tools are also shifting the patient’s role from a passive recipient of care to an active participant in their own health journey. This fosters a culture of shared decision-making and empowerment.
- The MyCare app on bedside tablets gives patients unprecedented access to their own health data, turning the hospital stay into a more transparent and collaborative experience.
- AI-powered physiotherapy trainers like AllyCare, an SGH partnership with a startup, allow patients to perform prescribed exercises at home. The system uses motion tracking to provide real-time feedback on posture and accuracy, enabling effective rehabilitation without multiple hospital visits .
This empowerment is a cornerstone of Singapore’s broader national shift towards population health and preventive care, where individuals are encouraged and equipped to take greater ownership of their well-being .

A Balanced Perspective: The Benefits and Hurdles of Building a Smart Hospital
The journey to create a fully integrated smart hospital ecosystem is ambitious and not without obstacles. A realistic assessment requires acknowledging both the transformative benefits and the significant challenges involved.
The Transformative Benefits
The advantages of the smart hospital model ripple across the entire healthcare system:
- For Patients: The primary gains are improved health outcomes through earlier diagnosis and personalized treatments. Patients also experience greater convenience, reduced waiting times, and a sense of empowerment from being more involved in their care.
- For Hospitals: The benefits include a dramatic increase in operational efficiency, optimized allocation of critical resources like beds and staff, and reduced clinician burnout from administrative overload. This ultimately enhances the hospital’s capacity to care for more patients effectively.
- For the System: At a macro level, this model enables the strategic shift from expensive, reactive hospital-centric care to more sustainable preventive and community-based models. By managing population health more proactively, it has the potential to lower long-term healthcare costs for the nation.
The Real-World Challenges and Singapore’s Solutions
Singapore’s progress offers a valuable case study in proactively addressing the hurdles inherent in digital transformation.
- Data Privacy & Security: In Smart Hospitals in Singapore, safeguarding patient data is paramount. With vast medical information stored digitally, cybersecurity is a top priority. The government addresses this through the Health Information Bill, secure government-managed clouds, and platforms like TRUST, which enable safe data analysis without extracting sensitive information—ensuring both innovation and privacy go hand in hand MOH, 2024; .
- High Implementation Costs & Integration: The transition to a smart hospital requires substantial upfront investment in infrastructure, technology, and training. The Singapore government plays a crucial role here, injecting funds like the S$200 million MOH Health Innovation Fund to support ground-up development and test-bedding of innovations .
- AI Bias and Accountability: Smart Hospitals in Singapore address the challenge of AI bias and accountability through a strong ethical framework. Since AI models trained on limited data can reinforce health inequalities, Singapore ensures fairness by using large, locally relevant datasets—like the 7,000 patients in the CKD digital twin project—and enforcing strict validation and monitoring to maintain accuracy, transparency, and patient safety.
- Clinician and Patient Adoption: Technology is only effective if it is used. A 2021 Accenture survey revealed that while interest is present, adoption of digital health tools in Singapore has room to grow. For instance, 43% of Singaporeans had not used digital tech to manage their health in the past year, and only 8% had a virtual care appointment. Barriers include concerns about data security, cost, and a lack of awareness or training . Singapore addresses this through change management programs, user-friendly design (like the MyCare app), and demonstrating clear value to both patients and staff.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What truly defines one of the smart hospitals in Singapore?
A:Smart Hospitals in Singapore are not just about advanced gadgets—they represent an integrated, system-wide strategy that blends AI, robotics, and IoT with a patient-centric philosophy. This approach transforms three core areas of healthcare: improving clinical outcomes, enhancing patient and staff experiences, and streamlining hospital management for greater efficiency. The result is a truly holistic model of smart, sustainable care delivery.
Q2: Will AI and robots replace my doctor or nurse?
A: No. The model in Singapore is designed to augment, not replace, human clinicians. Technologies like AI and robotics handle data-intensive, repetitive, or physically demanding tasks. This frees up doctors and nurses to focus on complex decision-making, patient communication, and the empathetic, human aspects of care that machines cannot replicate.
Q3: How is patient data kept secure in such a connected system?
A: Security is a top priority, addressed through a multi-layered strategy. This includes robust legislation (the Health Information Bill), storing data on dedicated government-managed clouds (like HEALIX), strict data anonymization standards for research (via the TRUST platform), and limiting internet access on office devices to prevent breaches.
Q4: Is this model of care more expensive for patients?
A: Though the upfront cost of digital transformation is high, Smart Hospitals in Singapore are designed for long-term efficiency and affordability. By focusing on preventive care such as early CKD detection, home-based models like SGH@Home, and smarter hospital operations, Singapore is reducing overall healthcare expenses. Continued government subsidies also ensure these innovations remain accessible and affordable for all citizens.
Conclusion: Lessons from the Lion City for Global Healthcare
The journey of **smart hospitals in Singapore** offers more than just a showcase of futuristic technology; it provides a tangible blueprint for the future of healthcare delivery worldwide. Its success is not accidental but is built upon a powerful and deliberate combination of strategic pillars.
Key Takeaways from the Singapore Model
- Strong Government Vision & Investment: The transformation is driven by a top-down strategic push from the Ministry of Health, backed by significant public funding and clear national goals.
- An Integrated Ecosystem: Success hinges on deep collaboration between public hospitals (SGH, NUHS), research institutes, and national tech agencies like Synapxe, creating a cohesive innovation pipeline.
- A ‘Phygital’ Approach: The model masterfully blends digital innovation with physical care, extending services beyond hospital walls into the community and home, creating a true continuum of care.
- A Human-Centric Focus: At its core, the strategy prioritizes the empowerment of both patients and clinicians, ensuring that technology serves to enhance, not replace, the human element of medicine.
Actionable Insights for a Global Audience
For those looking to learn from Singapore’s example, the lessons are clear:
- For Healthcare Leaders: Technology adoption must be problem-driven, not technology-led. Start by identifying clear clinical or operational pain points and seek solutions that deliver demonstrable value. Fostering a culture of innovation and change management is as important as the technology itself.
- For Policymakers: A national digital health strategy is paramount. This requires supportive funding
mechanisms, robust regulatory frameworks for data governance and AI ethics, and public-private partnerships to accelerate innovation. - For Investors & Tech Companies: The greatest opportunities lie not in standalone gadgets, but in integrated solutions that fit seamlessly into clinical workflows. Demonstrating clear ROI—whether in improved patient outcomes, enhanced efficiency, or cost savings—is the key to adoption.
The transformation of Singapore’s healthcare system is a bold, ongoing experiment that offers a compelling glimpse into the future. It proves that with vision, investment, and a relentless focus on human-centric design, technology can be harnessed to build a healthcare system that is not only smarter but also more sustainable and profoundly more human.
The transformation of Singapore’s healthcare system offers a compelling glimpse into the future. What aspect of this model do you find most promising or challenging for your own region? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
